

- #Long path tool 5.2.1 validation key generator#
- #Long path tool 5.2.1 validation key password#
- #Long path tool 5.2.1 validation key plus#
Using this key, the TGS decrypts message D (authenticator) and sends the following 2 messages:ġ.
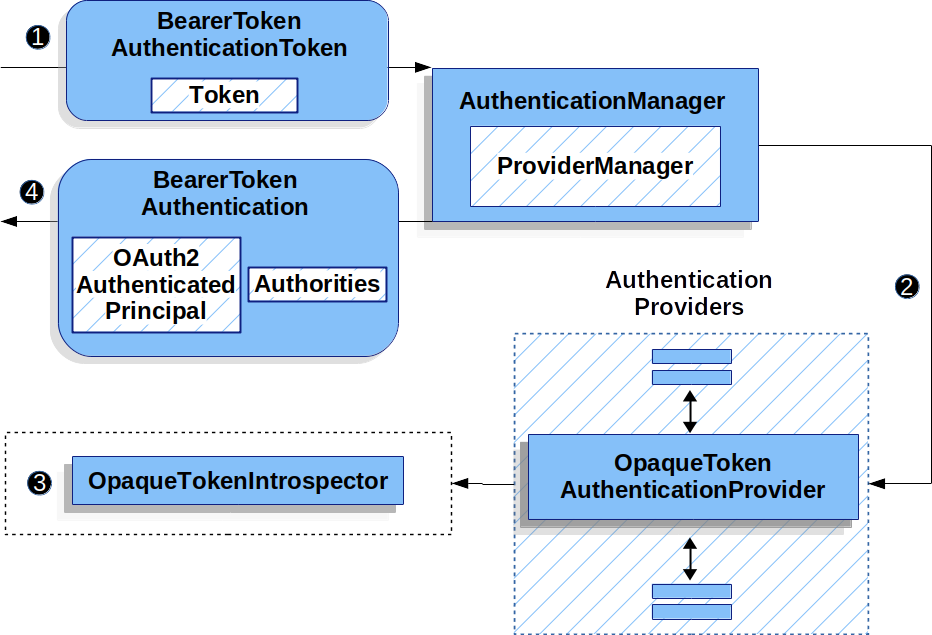
This gives it the "client/TGS session key". It decrypts message B using the TGS secret key. I) Upon receiving messages C and D, the TGS retrieves message B out of message C. Message D: Authenticator (which is composed of the client ID and the timestamp), encrypted using the Client/TGS Session Key Message C: Composed of the TGT from message B and the ID of the requested serviceĢ. H) When requesting services, the client sends the following messages to the TGS:ġ. G) The server provides the requested services to the client. If so, then the client can trust the server and start issuing service requests to the server. "Message H: the timestamp found in the client's authenticator"į) The client decrypts the confirmation (message H) using the Client/Server Session key and checks whether the timestamp is correct. Using the sessions key, SS decrypts the authenticator and sends the following message to the client to confirm its true identity and willingness to serve the client: Message G: A new authenticator, which includes the client ID, timestamp and is encrypted using Client/Server Session KeyĮ) The SS decrypts the ticket (message E) using its own secret key to retrieve the Client/Server Session Key. Message E from the previous step (the client-to-server ticket, encrypted using a service's secret key.)Ģ. The client connects to the SS and sends the following 2 messages:ġ. Message B is encrypted with the TGS secret key and cannot be decrypted by the clientĭ) Upon receiving messages E and F from the TGS, the client has enough information to authenticate itself to the Service Server (SS).
If it does work, then message A contains the Client/TGS session key that can be used for communications with the TGS.
#Long path tool 5.2.1 validation key password#
If the entered password does not match the password the AS found in the database, the hashes won't atch, and the decryption won't work. TGT includes client ID, client network address, validity periodī) The messages are encrypted using the key the AS generatedĬ) The user attempts to decrypt message A with the secret key generated by the client hashing the users entered password. CLIENT/TGS Session Key encrypted with secret key of clientĢ.
#Long path tool 5.2.1 validation key generator#
I) The public key is a point in the curve, obtained by multiplying the private key with the generator point (called G)Ī) AS generates a secret key by creating a hash of the user password, then sends 2 messages to client:ġ.
#Long path tool 5.2.1 validation key plus#
H) All the points which satisfy the equation plus a point at infinity lies on the elliptic curve G) An elliptic curve is the set of solutions to the equation given above Allows their use for protecting information classified up to top secret with 384-bit keysį) Based on equations of the form y^2 = x^3 +Ax + B along with a distinguished point at infinity, denoted They include schemes based on it in its Suite B set of recommended algorithmsĢ. A) First described in 1985 by Victor Miller (IBM) and Neil Koblitz (University of Washington)ī) Its security is based on the fact that finding the discrete logarithm of a random elliptic curve element with respect to a publicly-known base point is difficult to the point of being impractical to doĬ) The size of the elliptic curve determines the difficulty of finding the algorithmĭ) Level of security afforded by an RSA-based system with a large modulus can be achieved with a much smaller ECC groupġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
